ASIF: ASI, ENEA, INFN agreements
Asi Supported Irradiation Facilities (ASIF)

Website latest update on September 15, 2025
Together with geomagnetically trapped particles and galactic cosmic rays, solar protons (and other ions, electrons) can pose a hazard to both manned spaceflight and the sensitive components used in satellite subsystems and instrumentation. The physical mechanisms for radiation-induced damages have been investigated for many decades. They are related, for instance, to the type of particle and its energy, the device type, and its material composition (e.g., see SR-NIEL Framework: Physics Handbook). The ASIF website was initially created in September 2018.
Similarly to other radiation environments, in space radiation environment electronic devices undergo radiation damage induced by both cumulative and single event effects, i.e.,
- single event effects (SEE) - due to a highly ionizing dose deposition caused by a single high energy particle occurring in a sensitive region of a device - can occur at any time and with short time response;
- total ionizing dose (TID) effects - due to the accumulation of ionizing dose deposition over a long time - are a long term effects and uniformly affect all sensitive devices;
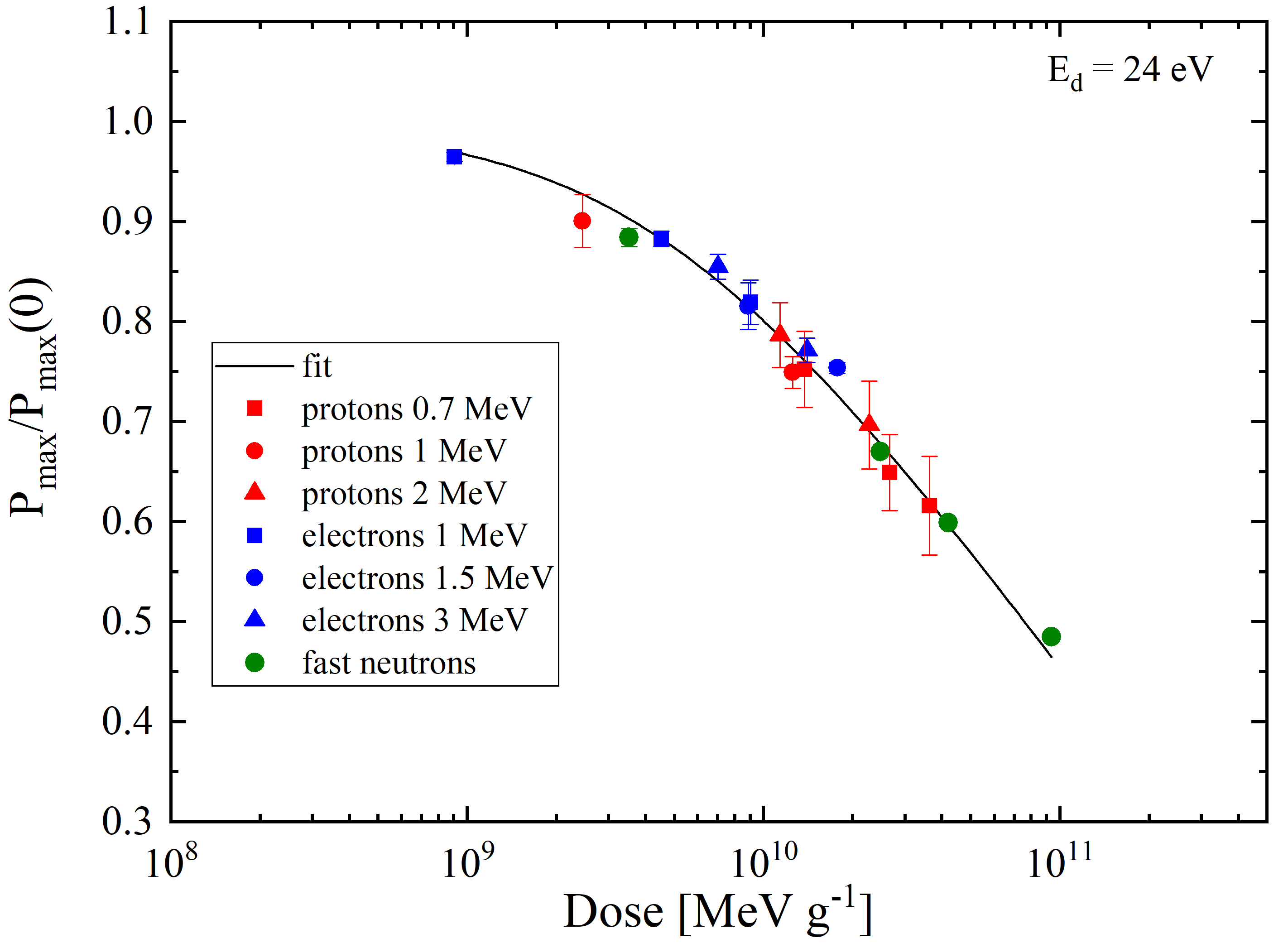
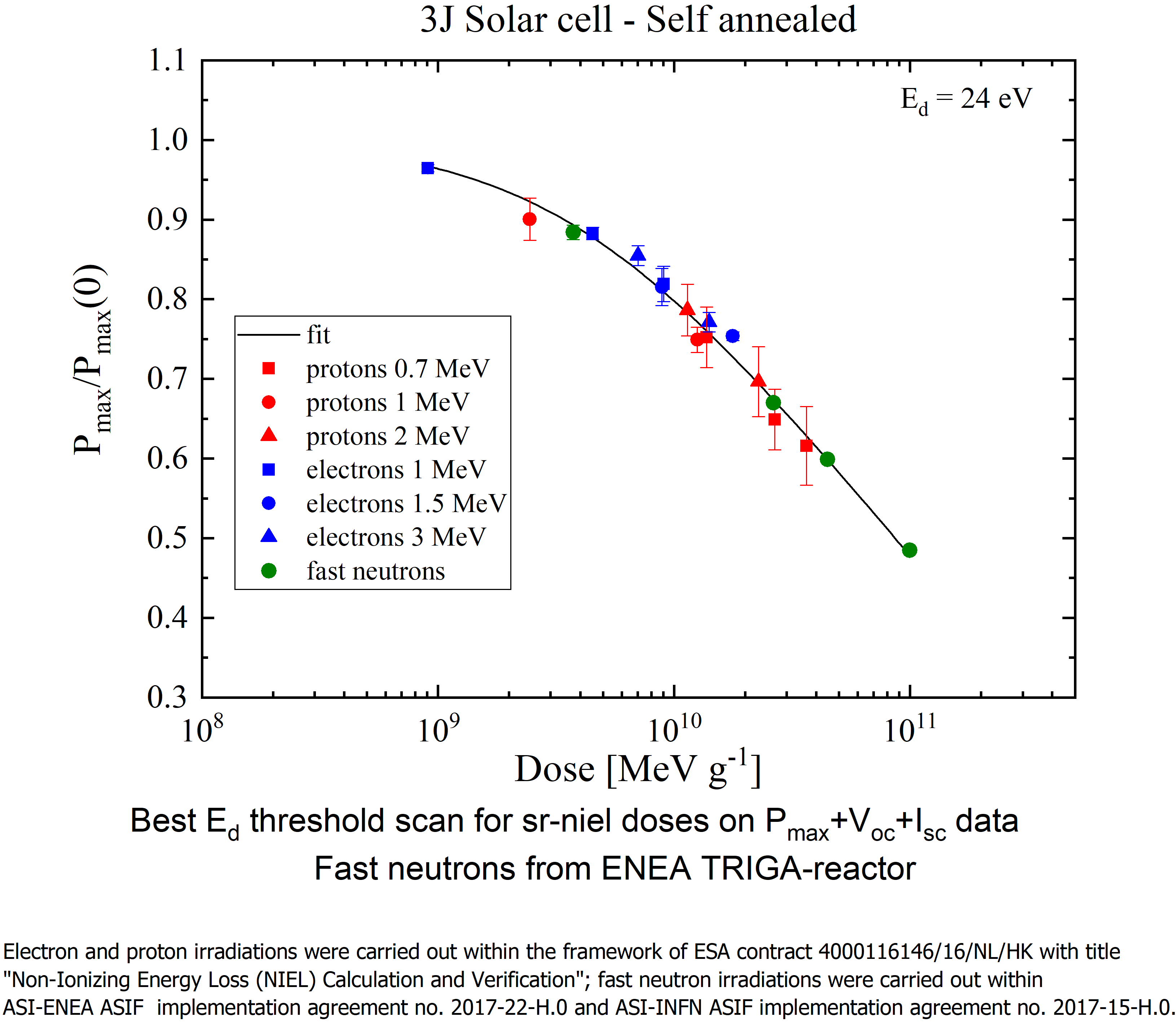
- displacement damage (TNID) effects – due to the accumulation of crystal lattice defects over a long time – are long term effects and uniformly affect all sensitive devices.
In sr-niel (ASIF relatated) website, there are calculators available for i) determining ionizing doses (TIDs), ii) non-ionizing doses (TNIDs) and iii) SEEs (single event effect).
ASIF program, as formulated by ASI (see this webpage), aims to establish an interactive coordinated set of the irradiation facilities, throughout the national territory, serving the national and international space communities. In fact, at national level industrial and institutional/research assets and centers in the field of EEE need to be coordinated, supported and represented at international level.
Italy has a long experience in the field of electronics devices design, manufacturing and utilization for various market sectors and in particular for Space. For instance, in the last years some project have been implemented in the field of GaAs/GaN EEE for consolidating the presence of the National GaN supply chain in the european context, thus achieving the role of second european source.
In the above context, the core elements of the supply chain are the availability of dedicated infrastructures like foundries, design centers, testing facilities and research centers and, finally, irradiation facilities.
Furthermore, it is worth to remark that the knowledge of space radiation environment, in general, is a driving element for:
- focusing the investigation of radiation damage,
- developing treatment/transport/simulation tools, and modelling particle fluxes and their transport to predict TNID, TID and SEEs and, thus, the expected operating conditions of devices in space ratiation environment,
- evaluating radiation impact on devices and their qualification, in view of their operation in space for both orbital and deep space missions.
ASIF agreements were established based on the consolidated concept that the development of future generation of EEE components is or is expected to be a key strategic area of interest for future Investments. Further information on radiation damage assessment for space missions is available at webpage.
From version 3.1.6, the ASIF website is operated by a virtual server in VDC (Virtual Data Center) environment at the Italian Space Agency, ASI.
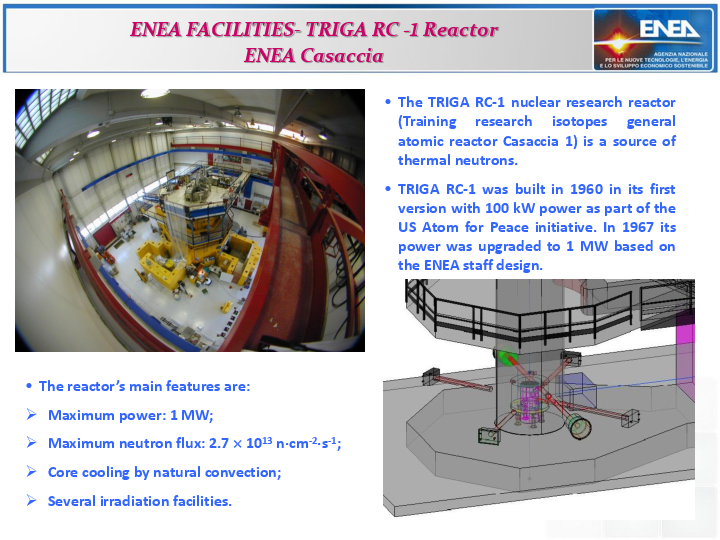
Following ASIF implementation agreements 2017-22-HD.0 ASI-ENEA, 2017-15-HD.0 ASI-INFN, 2021-39-HH.0 ASI-ENEA, 2021-36 HH.0 ASI-University of Milano-Bicocca and 2024-21-HH ASI-INFN, the ASIF and ASIF gateway websites, the sr-niel, helmod and geomagsphere websites are mantained within the space radiation environment activities of ASIF framework. Their websevers are handled by means of ASIF support center at the Physics Department of Milano-Bicocca University and are operated by virtual servers at the Italian Space Agency, ASI.